Physical Activity Guidelines

What do Activity Guidelines do? These recommendations are based on the best available evidence, assessing the balance between harms and benefits in the context of social and economic equity, acceptability, and feasibility. The strength of a recommendation is assessed using the GRADE (Graded Assessment of Evidence, Development, and Evaluation) framework. The strength rating of an activity recommendation is based on evidence quality, sensitivity to values, and acceptability, feasibility, and resource implications.
Since 2008, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has issued an updated set of Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. The guidelines are based on a comprehensive review of scientific research and are targeted at health professionals, and policymakers, as well as the general public. HHS also has created a consumer-friendly communication campaign called Move Your Way to provide tools and resources for the public. Using these guidelines is critical to improving the health and well-being of all Americans.
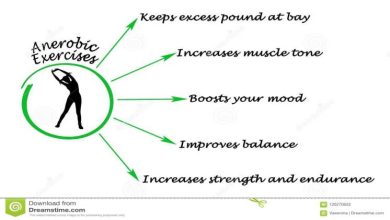
According to the activity guidelines, most adults should perform at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous-intensity physical activity every week. In addition to aerobic exercise, adults with chronic conditions should engage in activities that are safe for them. These activities should include muscle-strengthening exercises, which engage all major muscle groups and provide additional health benefits. It is also important to consult a physician or physical activity specialist before engaging in vigorous physical activity.